
|
Computational Toolsmiths
Software Tools for Computational Science, Engineering, and Medicine |
FirWav Complex Orthogonal Filters
- Examples of Individual Filters
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Symmetric (DCOMS)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Symmetric (DCOLS)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Asymmetric (DCOMA)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Asymmetric (DCOLA)
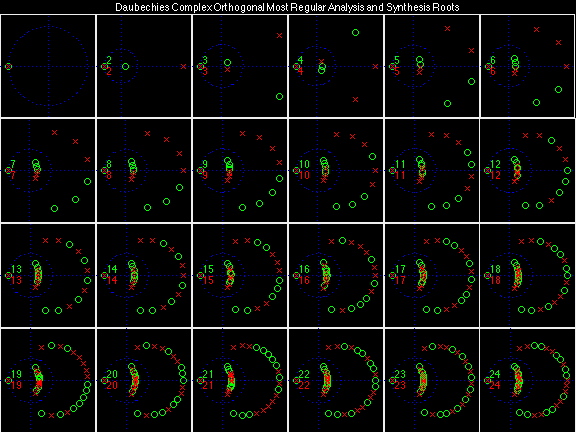
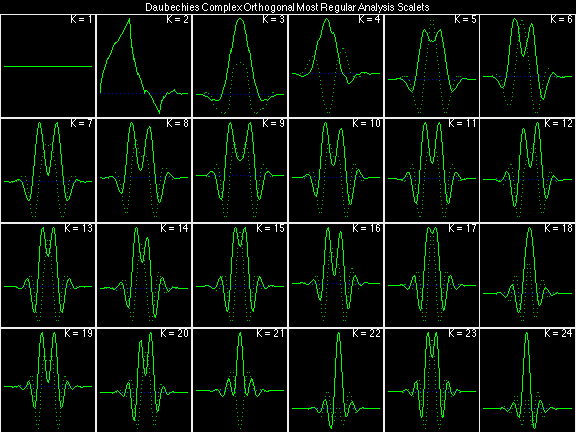
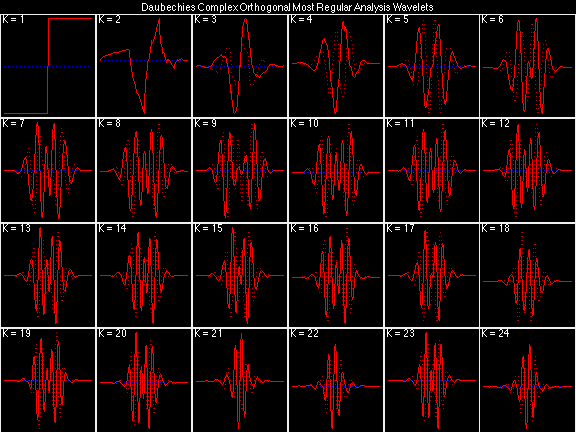
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Regular (DCOMR)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Uncertain (DCOLU)
- Examples of Filter Families
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Asymmetric (DCOLA)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Asymmetric (DCOMA)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Disjoint (DCOLD)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Disjoint (DCOMD)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Regular (DCOLR)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Regular (DCOMR)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Symmetric (DCOLS)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Symmetric (DCOMS)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Uncertain (DCOLU)
- Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Uncertain (DCOMU)
- Web Site Page Directory
Examples of Individual Filters
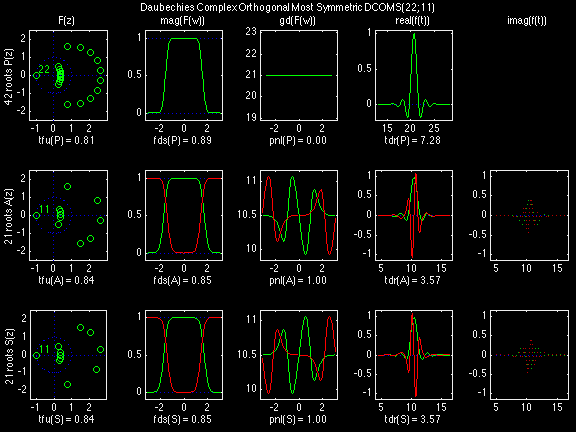
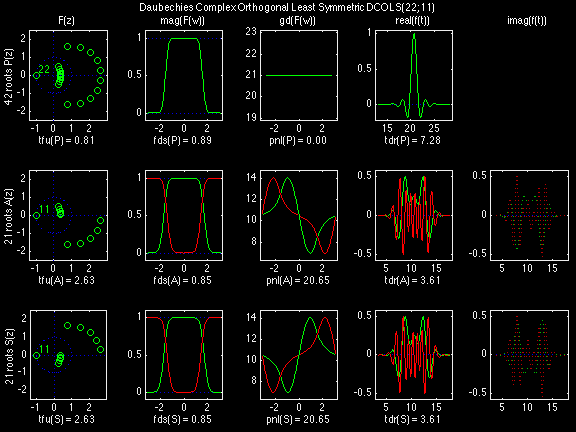
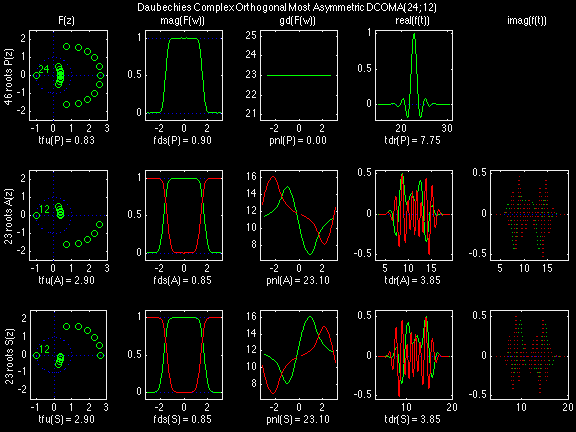
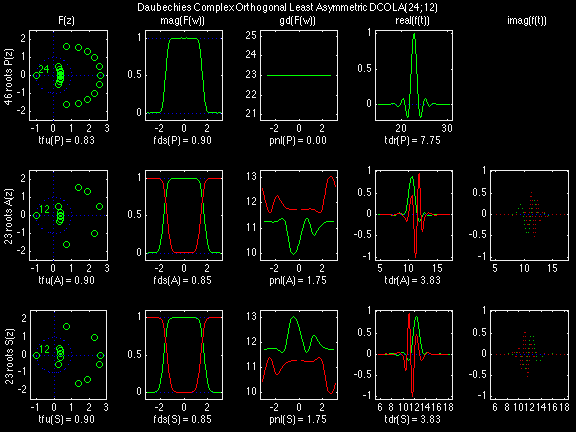
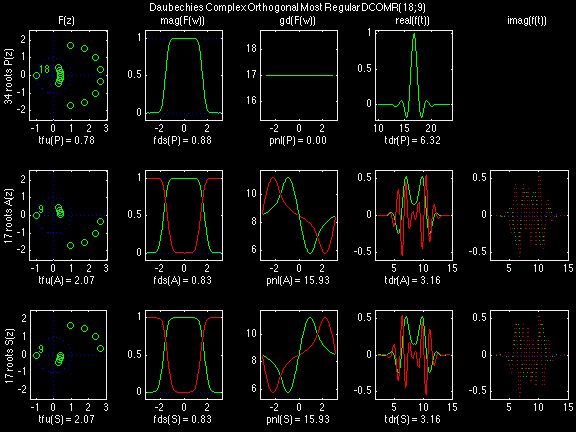
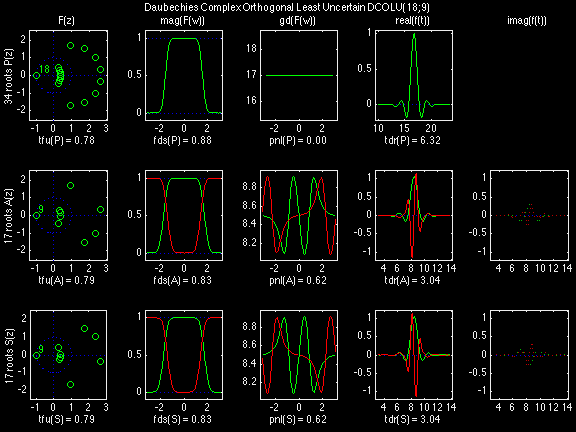
In the following examples of filters, each figure contains a matrix of subplots with rows corresponding to product, analysis, and synthesis filters, and with columns corresponding to characteristics of the filters in the complex z domain, the frequency domain, and the time domain.
Figure legend abbreviations for the plots on this page include:
- f(t) = filter in time t domain;
- F(z) = filter in complex z domain;
- F(w) = filter in frequency w domain;
- mag(F) = magnitude of F(w);
- db(F) = magnitude of F(w) in decibels;
- ang(F) = phase angle of F(w);
- up(F) = unwrapped phase angle of F(w);
- pd(F) = phase delay of F(w);
- gd(F) = group delay of F(w);
- P(z) = Product filter;
- A(z) = Analysis filter, primary spectral factor of P(z);
- S(z) = Synthesis filter, complementary spectral factor of P(z);
- tfu = Time-Frequency Uncertainty;
- tdr = Time-Domain Regularity;
- fds = Frequency-Domain Selectivity; and
- pnl = total Phase NonLinearity.
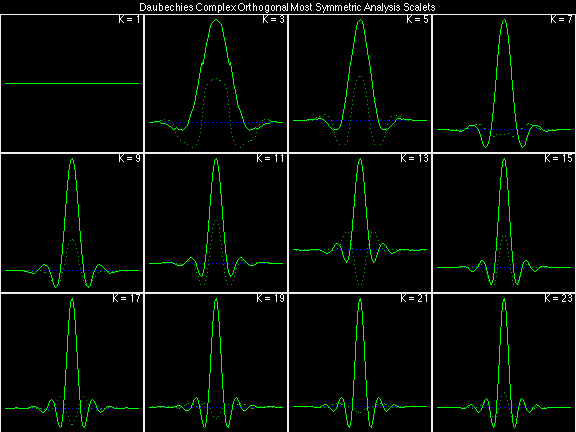
Scalets (lowpass filters) are in green; wavelets (highpass filters) are in red. In the z domain plots, the number near the zero at z = -1 indicates the multiplicity of that zero. This number determines the theoretical number of vanishing moments of the corresponding wavelet filter.
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Symmetric (DCOMS)
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Symmetric (DCOLS)
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Asymmetric (DCOMA)
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Asymmetric (DCOLA)
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Regular (DCOMR)
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Uncertain (DCOLU)
Examples of Filter Families
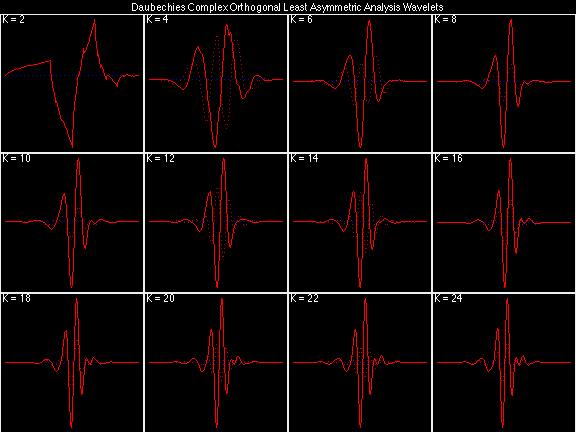
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Asymmetric (DCOLA)
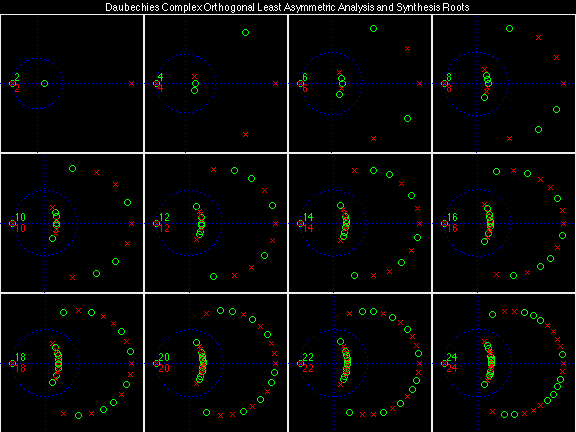
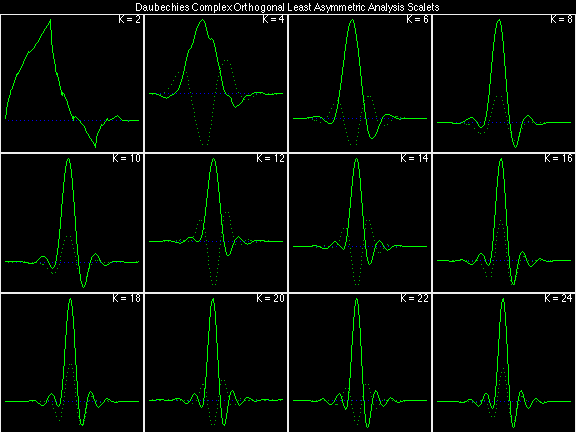
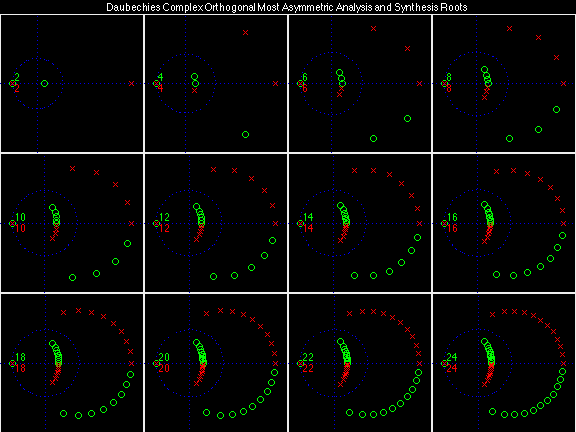
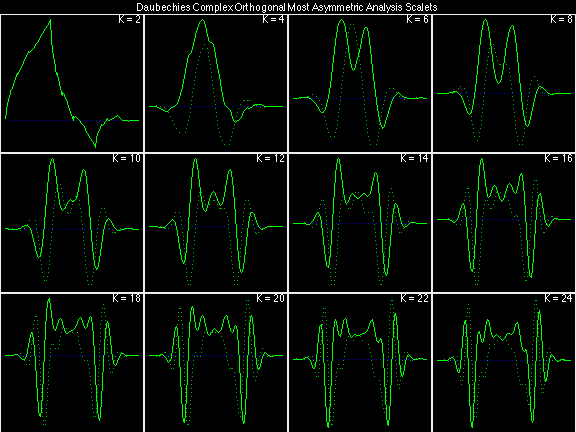
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Asymmetric (DCOMA)

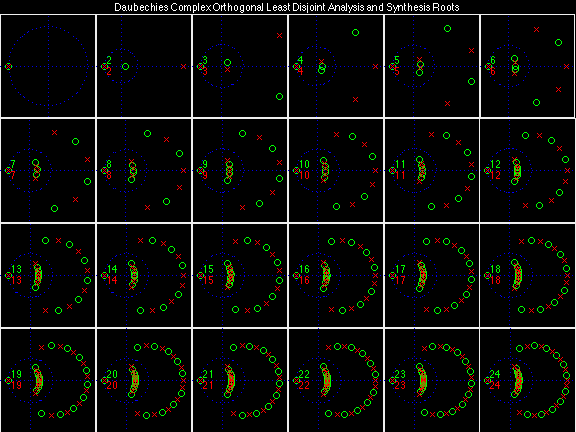
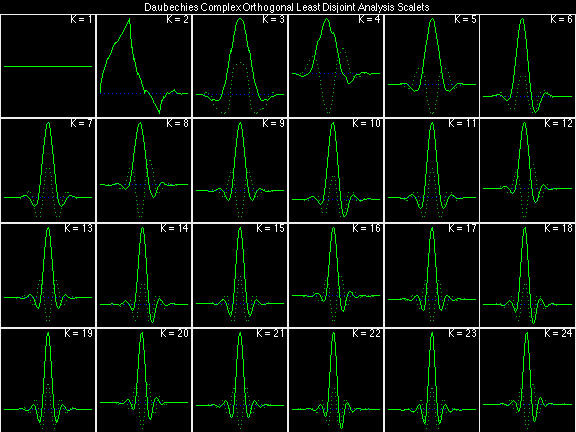
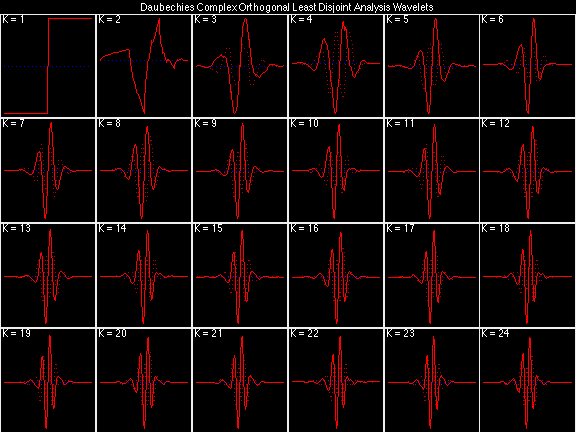
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Disjoint (DCOLD)
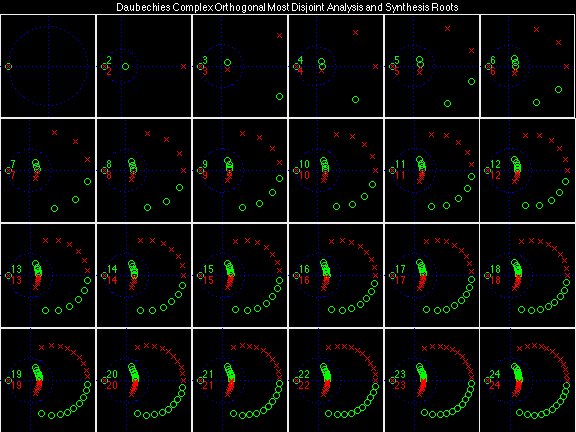
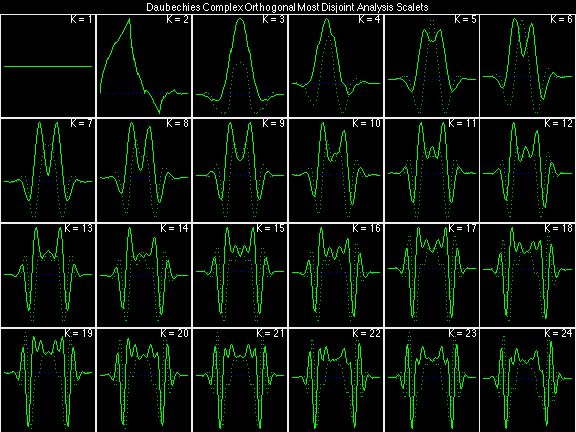
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Disjoint (DCOMD)
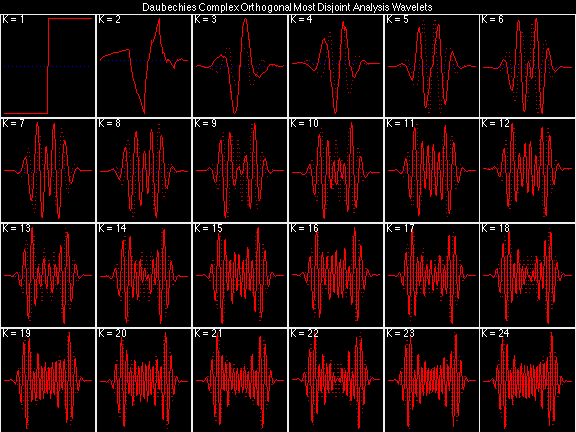
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Regular (DCOLR)



Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Regular (DCOMR)
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Symmetric (DCOLS)
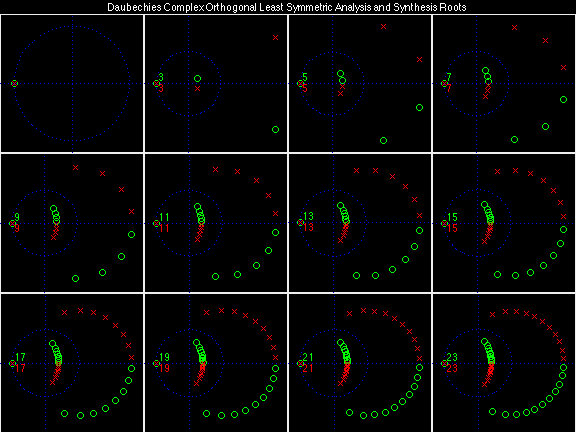
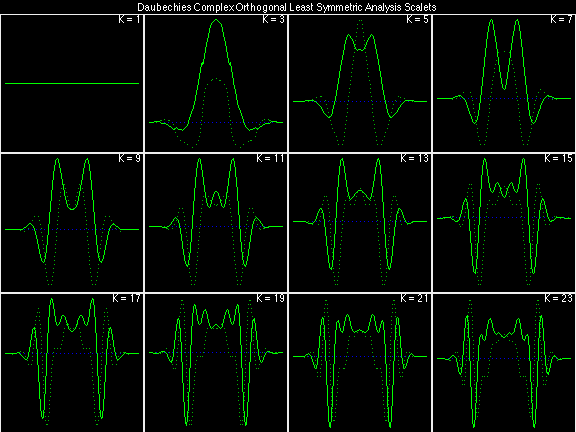
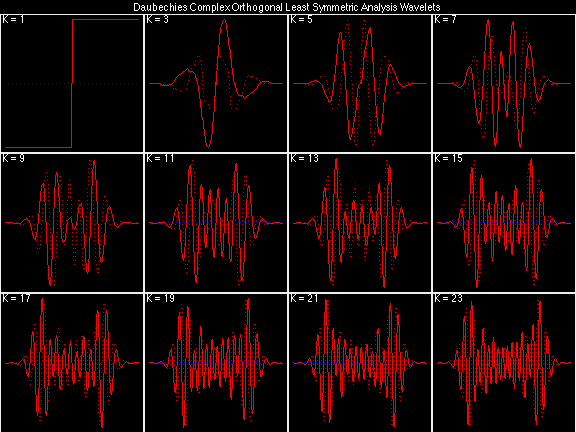
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Symmetric (DCOMS)


Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Least Uncertain (DCOLU)
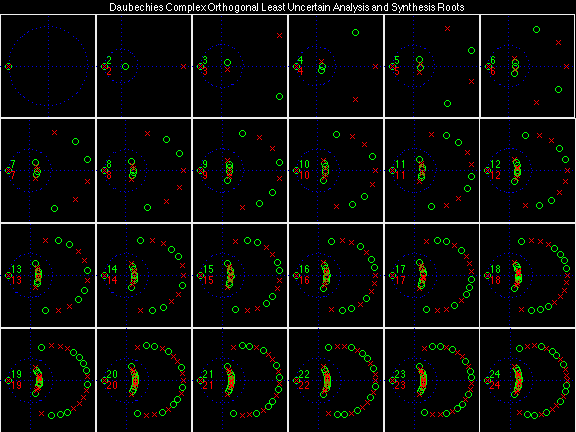
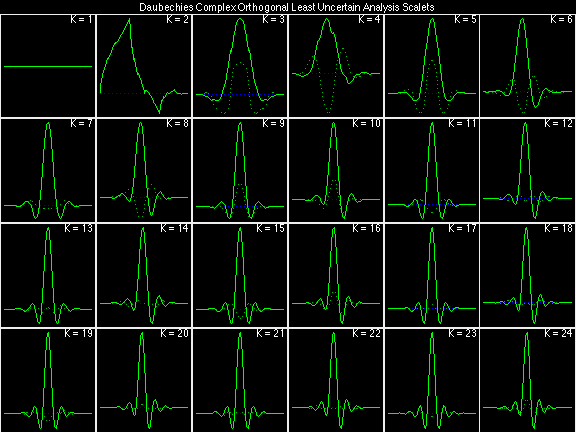
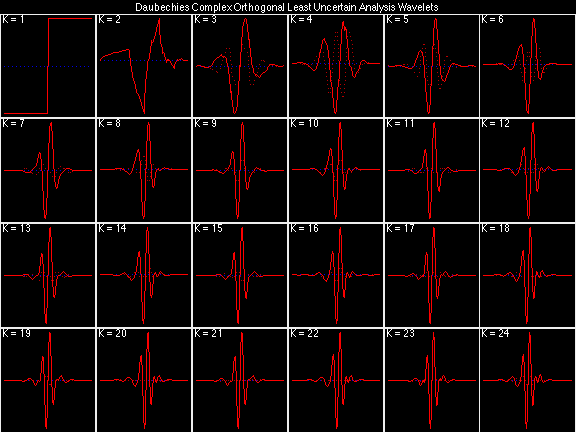
Daubechies Complex Orthogonal Most Uncertain (DCOMU)


